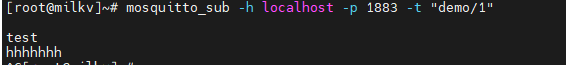
实际使用时,需要客户端提供密码,才能连接,更新下配置文件。
# Config file for mosquitto
#
# See mosquitto.conf(5) for more information.
#
# Default values are shown, uncomment to change.
#
# Use the # character to indicate a comment, but only if it is the
# very first character on the line.
# =================================================================
# General configuration
# =================================================================
# Use per listener security settings.
#
# It is recommended this option be set before any other options.
#
# If this option is set to true, then all authentication and access control
# options are controlled on a per listener basis. The following options are
# affected:
#
# acl_file
# allow_anonymous
# allow_zero_length_clientid
# auto_id_prefix
# password_file
# plugin
# plugin_opt_*
# psk_file
#
# Note that if set to true, then a durable client (i.e. with clean session set
# to false) that has disconnected will use the ACL settings defined for the
# listener that it was most recently connected to.
#
# The default behaviour is for this to be set to false, which maintains the
# setting behaviour from previous versions of mosquitto.
#per_listener_settings false
# This option controls whether a client is allowed to connect with a zero
# length client id or not. This option only affects clients using MQTT v3.1.1
# and later. If set to false, clients connecting with a zero length client id
# are disconnected. If set to true, clients will be allocated a client id by
# the broker. This means it is only useful for clients with clean session set
# to true.
#allow_zero_length_clientid true
# If allow_zero_length_clientid is true, this option allows you to set a prefix
# to automatically generated client ids to aid visibility in logs.
# Defaults to 'auto-'
#auto_id_prefix auto-
# This option affects the scenario when a client subscribes to a topic that has
# retained messages. It is possible that the client that published the retained
# message to the topic had access at the time they published, but that access
# has been subsequently removed. If check_retain_source is set to true, the
# default, the source of a retained message will be checked for access rights
# before it is republished. When set to false, no check will be made and the
# retained message will always be published. This affects all listeners.
#check_retain_source true
# QoS 1 and 2 messages will be allowed inflight per client until this limit
# is exceeded. Defaults to 0. (No maximum)
# See also max_inflight_messages
#max_inflight_bytes 0
# The maximum number of QoS 1 and 2 messages currently inflight per
# client.
# This includes messages that are partway through handshakes and
# those that are being retried. Defaults to 20. Set to 0 for no
# maximum. Setting to 1 will guarantee in-order delivery of QoS 1
# and 2 messages.
#max_inflight_messages 20
# For MQTT v5 clients, it is possible to have the server send a "server
# keepalive" value that will override the keepalive value set by the client.
# This is intended to be used as a mechanism to say that the server will
# disconnect the client earlier than it anticipated, and that the client should
# use the new keepalive value. The max_keepalive option allows you to specify
# that clients may only connect with keepalive less than or equal to this
# value, otherwise they will be sent a server keepalive telling them to use
# max_keepalive. This only applies to MQTT v5 clients. The default, and maximum
# value allowable, is 65535.
#
# Set to 0 to allow clients to set keepalive = 0, which means no keepalive
# checks are made and the client will never be disconnected by the broker if no
# messages are received. You should be very sure this is the behaviour that you
# want.
#
# For MQTT v3.1.1 and v3.1 clients, there is no mechanism to tell the client
# what keepalive value they should use. If an MQTT v3.1.1 or v3.1 client
# specifies a keepalive time greater than max_keepalive they will be sent a
# CONNACK message with the "identifier rejected" reason code, and disconnected.
#
#max_keepalive 65535
# For MQTT v5 clients, it is possible to have the server send a "maximum packet
# size" value that will instruct the client it will not accept MQTT packets
# with size greater than max_packet_size bytes. This applies to the full MQTT
# packet, not just the payload. Setting this option to a positive value will
# set the maximum packet size to that number of bytes. If a client sends a
# packet which is larger than this value, it will be disconnected. This applies
# to all clients regardless of the protocol version they are using, but v3.1.1
# and earlier clients will of course not have received the maximum packet size
# information. Defaults to no limit. Setting below 20 bytes is forbidden
# because it is likely to interfere with ordinary client operation, even with
# very small payloads.
#max_packet_size 0
# QoS 1 and 2 messages above those currently in-flight will be queued per
# client until this limit is exceeded. Defaults to 0. (No maximum)
# See also max_queued_messages.
# If both max_queued_messages and max_queued_bytes are specified, packets will
# be queued until the first limit is reached.
#max_queued_bytes 0
# Set the maximum QoS supported. Clients publishing at a QoS higher than
# specified here will be disconnected.
#max_qos 2
# The maximum number of QoS 1 and 2 messages to hold in a queue per client
# above those that are currently in-flight. Defaults to 1000. Set
# to 0 for no maximum (not recommended).
# See also queue_qos0_messages.
# See also max_queued_bytes.
#max_queued_messages 1000
#
# This option sets the maximum number of heap memory bytes that the broker will
# allocate, and hence sets a hard limit on memory use by the broker. Memory
# requests that exceed this value will be denied. The effect will vary
# depending on what has been denied. If an incoming message is being processed,
# then the message will be dropped and the publishing client will be
# disconnected. If an outgoing message is being sent, then the individual
# message will be dropped and the receiving client will be disconnected.
# Defaults to no limit.
#memory_limit 0
# This option sets the maximum publish payload size that the broker will allow.
# Received messages that exceed this size will not be accepted by the broker.
# The default value is 0, which means that all valid MQTT messages are
# accepted. MQTT imposes a maximum payload size of 268435455 bytes.
#message_size_limit 0
# This option allows the session of persistent clients (those with clean
# session set to false) that are not currently connected to be removed if they
# do not reconnect within a certain time frame. This is a non-standard option
# in MQTT v3.1. MQTT v3.1.1 and v5.0 allow brokers to remove client sessions.
#
# Badly designed clients may set clean session to false whilst using a randomly
# generated client id. This leads to persistent clients that connect once and
# never reconnect. This option allows these clients to be removed. This option
# allows persistent clients (those with clean session set to false) to be
# removed if they do not reconnect within a certain time frame.
#
# The expiration period should be an integer followed by one of h d w m y for
# hour, day, week, month and year respectively. For example
#
# persistent_client_expiration 2m
# persistent_client_expiration 14d
# persistent_client_expiration 1y
#
# The default if not set is to never expire persistent clients.
#persistent_client_expiration
# Write process id to a file. Default is a blank string which means
# a pid file shouldn't be written.
# This should be set to /var/run/mosquitto/mosquitto.pid if mosquitto is
# being run automatically on boot with an init script and
# start-stop-daemon or similar.
#pid_file /var/run/mosquitto.pid
# Set to true to queue messages with QoS 0 when a persistent client is
# disconnected. These messages are included in the limit imposed by
# max_queued_messages and max_queued_bytes
# Defaults to false.
# This is a non-standard option for the MQTT v3.1 spec but is allowed in
# v3.1.1.
#queue_qos0_messages false
# Set to false to disable retained message support. If a client publishes a
# message with the retain bit set, it will be disconnected if this is set to
# false.
#retain_available true
# Disable Nagle's algorithm on client sockets. This has the effect of reducing
# latency of individual messages at the potential cost of increasing the number
# of packets being sent.
#set_tcp_nodelay false
# Time in seconds between updates of the $SYS tree.
# Set to 0 to disable the publishing of the $SYS tree.
sys_interval 5
# The MQTT specification requires that the QoS of a message delivered to a
# subscriber is never upgraded to match the QoS of the subscription. Enabling
# this option changes this behaviour. If upgrade_outgoing_qos is set true,
# messages sent to a subscriber will always match the QoS of its subscription.
# This is a non-standard option explicitly disallowed by the spec.
#upgrade_outgoing_qos false
# When run as root, drop privileges to this user and its primary
# group.
# Set to root to stay as root, but this is not recommended.
# If set to "mosquitto", or left unset, and the "mosquitto" user does not exist
# then it will drop privileges to the "nobody" user instead.
# If run as a non-root user, this setting has no effect.
# Note that on Windows this has no effect and so mosquitto should be started by
# the user you wish it to run as.
user nobody
# =================================================================
# Listeners
# =================================================================
# Listen on a port/ip address combination. By using this variable
# multiple times, mosquitto can listen on more than one port. If
# this variable is used and neither bind_address nor port given,
# then the default listener will not be started.
# The port number to listen on must be given. Optionally, an ip
# address or host name may be supplied as a second argument. In
# this case, mosquitto will attempt to bind the listener to that
# address and so restrict access to the associated network and
# interface. By default, mosquitto will listen on all interfaces.
# Note that for a websockets listener it is not possible to bind to a host
# name.
#
# On systems that support Unix Domain Sockets, it is also possible
# to create a # Unix socket rather than opening a TCP socket. In
# this case, the port number should be set to 0 and a unix socket
# path must be provided, e.g.
# listener 0 /tmp/mosquitto.sock
#
# listener port-number [ip address/host name/unix socket path]
listener 1883
# By default, a listener will attempt to listen on all supported IP protocol
# versions. If you do not have an IPv4 or IPv6 interface you may wish to
# disable support for either of those protocol versions. In particular, note
# that due to the limitations of the websockets library, it will only ever
# attempt to open IPv6 sockets if IPv6 support is compiled in, and so will fail
# if IPv6 is not available.
#
# Set to `ipv4` to force the listener to only use IPv4, or set to `ipv6` to
# force the listener to only use IPv6. If you want support for both IPv4 and
# IPv6, then do not use the socket_domain option.
#
#socket_domain
# Bind the listener to a specific interface. This is similar to
# the [ip address/host name] part of the listener definition, but is useful
# when an interface has multiple addresses or the address may change. If used
# with the [ip address/host name] part of the listener definition, then the
# bind_interface option will take priority.
# Not available on Windows.
#
# Example: bind_interface eth0
#bind_interface
# When a listener is using the websockets protocol, it is possible to serve
# http data as well. Set http_dir to a directory which contains the files you
# wish to serve. If this option is not specified, then no normal http
# connections will be possible.
#http_dir
# The maximum number of client connections to allow. This is
# a per listener setting.
# Default is -1, which means unlimited connections.
# Note that other process limits mean that unlimited connections
# are not really possible. Typically the default maximum number of
# connections possible is around 1024.
#max_connections -1
# The listener can be restricted to operating within a topic hierarchy using
# the mount_point option. This is achieved be prefixing the mount_point string
# to all topics for any clients connected to this listener. This prefixing only
# happens internally to the broker; the client will not see the prefix.
#mount_point
# Choose the protocol to use when listening.
# This can be either mqtt or websockets.
# Certificate based TLS may be used with websockets, except that only the
# cafile, certfile, keyfile, ciphers, and ciphers_tls13 options are supported.
#protocol mqtt
# Set use_username_as_clientid to true to replace the clientid that a client
# connected with with its username. This allows authentication to be tied to
# the clientid, which means that it is possible to prevent one client
# disconnecting another by using the same clientid.
# If a client connects with no username it will be disconnected as not
# authorised when this option is set to true.
# Do not use in conjunction with clientid_prefixes.
# See also use_identity_as_username.
# This does not apply globally, but on a per-listener basis.
#use_username_as_clientid
# Change the websockets headers size. This is a global option, it is not
# possible to set per listener. This option sets the size of the buffer used in
# the libwebsockets library when reading HTTP headers. If you are passing large
# header data such as cookies then you may need to increase this value. If left
# unset, or set to 0, then the default of 1024 bytes will be used.
#websockets_headers_size
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Certificate based SSL/TLS support
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# The following options can be used to enable certificate based SSL/TLS support
# for this listener. Note that the recommended port for MQTT over TLS is 8883,
# but this must be set manually.
#
# See also the mosquitto-tls man page and the "Pre-shared-key based SSL/TLS
# support" section. Only one of certificate or PSK encryption support can be
# enabled for any listener.
# Both of certfile and keyfile must be defined to enable certificate based
# TLS encryption.
# Path to the PEM encoded server certificate.
#certfile
# Path to the PEM encoded keyfile.
#keyfile
# If you wish to control which encryption ciphers are used, use the ciphers
# option. The list of available ciphers can be optained using the "openssl
# ciphers" command and should be provided in the same format as the output of
# that command. This applies to TLS 1.2 and earlier versions only. Use
# ciphers_tls1.3 for TLS v1.3.
#ciphers
# Choose which TLS v1.3 ciphersuites are used for this listener.
# Defaults to "TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256:TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256"
#ciphers_tls1.3
# If you have require_certificate set to true, you can create a certificate
# revocation list file to revoke access to particular client certificates. If
# you have done this, use crlfile to point to the PEM encoded revocation file.
#crlfile
# To allow the use of ephemeral DH key exchange, which provides forward
# security, the listener must load DH parameters. This can be specified with
# the dhparamfile option. The dhparamfile can be generated with the command
# e.g. "openssl dhparam -out dhparam.pem 2048"
#dhparamfile
# By default an TLS enabled listener will operate in a similar fashion to a
# https enabled web server, in that the server has a certificate signed by a CA
# and the client will verify that it is a trusted certificate. The overall aim
# is encryption of the network traffic. By setting require_certificate to true,
# the client must provide a valid certificate in order for the network
# connection to proceed. This allows access to the broker to be controlled
# outside of the mechanisms provided by MQTT.
#require_certificate false
# cafile and capath define methods of accessing the PEM encoded
# Certificate Authority certificates that will be considered trusted when
# checking incoming client certificates.
# cafile defines the path to a file containing the CA certificates.
# capath defines a directory that will be searched for files
# containing the CA certificates. For capath to work correctly, the
# certificate files must have ".crt" as the file ending and you must run
# "openssl rehash <path to capath>" each time you add/remove a certificate.
#cafile
#capath
# If require_certificate is true, you may set use_identity_as_username to true
# to use the CN value from the client certificate as a username. If this is
# true, the password_file option will not be used for this listener.
#use_identity_as_username false
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Pre-shared-key based SSL/TLS support
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# The following options can be used to enable PSK based SSL/TLS support for
# this listener. Note that the recommended port for MQTT over TLS is 8883, but
# this must be set manually.
#
# See also the mosquitto-tls man page and the "Certificate based SSL/TLS
# support" section. Only one of certificate or PSK encryption support can be
# enabled for any listener.
# The psk_hint option enables pre-shared-key support for this listener and also
# acts as an identifier for this listener. The hint is sent to clients and may
# be used locally to aid authentication. The hint is a free form string that
# doesn't have much meaning in itself, so feel free to be creative.
# If this option is provided, see psk_file to define the pre-shared keys to be
# used or create a security plugin to handle them.
#psk_hint
# When using PSK, the encryption ciphers used will be chosen from the list of
# available PSK ciphers. If you want to control which ciphers are available,
# use the "ciphers" option. The list of available ciphers can be optained
# using the "openssl ciphers" command and should be provided in the same format
# as the output of that command.
#ciphers
# Set use_identity_as_username to have the psk identity sent by the client used
# as its username. Authentication will be carried out using the PSK rather than
# the MQTT username/password and so password_file will not be used for this
# listener.
#use_identity_as_username false
# =================================================================
# Persistence
# =================================================================
# If persistence is enabled, save the in-memory database to disk
# every autosave_interval seconds. If set to 0, the persistence
# database will only be written when mosquitto exits. See also
# autosave_on_changes.
# Note that writing of the persistence database can be forced by
# sending mosquitto a SIGUSR1 signal.
#autosave_interval 1800
# If true, mosquitto will count the number of subscription changes, retained
# messages received and queued messages and if the total exceeds
# autosave_interval then the in-memory database will be saved to disk.
# If false, mosquitto will save the in-memory database to disk by treating
# autosave_interval as a time in seconds.
#autosave_on_changes false
# Save persistent message data to disk (true/false).
# This saves information about all messages, including
# subscriptions, currently in-flight messages and retained
# messages.
# retained_persistence is a synonym for this option.
#persistence false
# The filename to use for the persistent database, not including
# the path.
#persistence_file mosquitto.db
# Location for persistent database.
# Default is an empty string (current directory).
# Set to e.g. /var/lib/mosquitto if running as a proper service on Linux or
# similar.
#persistence_location
# =================================================================
# Logging
# =================================================================
# Places to log to. Use multiple log_dest lines for multiple
# logging destinations.
# Possible destinations are: stdout stderr syslog topic file dlt
#
# stdout and stderr log to the console on the named output.
#
# syslog uses the userspace syslog facility which usually ends up
# in /var/log/messages or similar.
#
# topic logs to the broker topic '$SYS/broker/log/<severity>',
# where severity is one of D, E, W, N, I, M which are debug, error,
# warning, notice, information and message. Message type severity is used by
# the subscribe/unsubscribe log_types and publishes log messages to
# $SYS/broker/log/M/susbcribe or $SYS/broker/log/M/unsubscribe.
#
# The file destination requires an additional parameter which is the file to be
# logged to, e.g. "log_dest file /var/log/mosquitto.log". The file will be
# closed and reopened when the broker receives a HUP signal. Only a single file
# destination may be configured.
#
# The dlt destination is for the automotive `Diagnostic Log and Trace` tool.
# This requires that Mosquitto has been compiled with DLT support.
#
# Note that if the broker is running as a Windows service it will default to
# "log_dest none" and neither stdout nor stderr logging is available.
# Use "log_dest none" if you wish to disable logging.
log_dest file /var/log/mosquitto.log
# Types of messages to log. Use multiple log_type lines for logging
# multiple types of messages.
# Possible types are: debug, error, warning, notice, information,
# none, subscribe, unsubscribe, websockets, all.
# Note that debug type messages are for decoding the incoming/outgoing
# network packets. They are not logged in "topics".
#log_type error
#log_type warning
#log_type notice
#log_type information
# If set to true, client connection and disconnection messages will be included
# in the log.
connection_messages true
# If using syslog logging (not on Windows), messages will be logged to the
# "daemon" facility by default. Use the log_facility option to choose which of
# local0 to local7 to log to instead. The option value should be an integer
# value, e.g. "log_facility 5" to use local5.
#log_facility
# If set to true, add a timestamp value to each log message.
log_timestamp true
# Set the format of the log timestamp. If left unset, this is the number of
# seconds since the Unix epoch.
# This is a free text string which will be passed to the strftime function. To
# get an ISO 8601 datetime, for example:
# log_timestamp_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
log_timestamp_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
# Change the websockets logging level. This is a global option, it is not
# possible to set per listener. This is an integer that is interpreted by
# libwebsockets as a bit mask for its lws_log_levels enum. See the
# libwebsockets documentation for more details. "log_type websockets" must also
# be enabled.
#websockets_log_level 0
# =================================================================
# Security
# =================================================================
# If set, only clients that have a matching prefix on their
# clientid will be allowed to connect to the broker. By default,
# all clients may connect.
# For example, setting "secure-" here would mean a client "secure-
# client" could connect but another with clientid "mqtt" couldn't.
#clientid_prefixes
# Boolean value that determines whether clients that connect
# without providing a username are allowed to connect. If set to
# false then a password file should be created (see the
# password_file option) to control authenticated client access.
#
# Defaults to false, unless there are no listeners defined in the configuration
# file, in which case it is set to true, but connections are only allowed from
# the local machine.
allow_anonymous false
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Default authentication and topic access control
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Control access to the broker using a password file. This file can be
# generated using the mosquitto_passwd utility. If TLS support is not compiled
# into mosquitto (it is recommended that TLS support should be included) then
# plain text passwords are used, in which case the file should be a text file
# with lines in the format:
# username:password
# The password (and colon) may be omitted if desired, although this
# offers very little in the way of security.
#
# See the TLS client require_certificate and use_identity_as_username options
# for alternative authentication options. If a plugin is used as well as
# password_file, the plugin check will be made first.
password_file /etc/mosquitto/pwfile
# Access may also be controlled using a pre-shared-key file. This requires
# TLS-PSK support and a listener configured to use it. The file should be text
# lines in the format:
# identity:key
# The key should be in hexadecimal format without a leading "0x".
# If an plugin is used as well, the plugin check will be made first.
#psk_file
# Control access to topics on the broker using an access control list
# file. If this parameter is defined then only the topics listed will
# have access.
# If the first character of a line of the ACL file is a # it is treated as a
# comment.
# Topic access is added with lines of the format:
#
# topic [read|write|readwrite|deny] <topic>
#
# The access type is controlled using "read", "write", "readwrite" or "deny".
# This parameter is optional (unless <topic> contains a space character) - if
# not given then the access is read/write. <topic> can contain the + or #
# wildcards as in subscriptions.
#
# The "deny" option can used to explicity deny access to a topic that would
# otherwise be granted by a broader read/write/readwrite statement. Any "deny"
# topics are handled before topics that grant read/write access.
#
# The first set of topics are applied to anonymous clients, assuming
# allow_anonymous is true. User specific topic ACLs are added after a
# user line as follows:
#
# user <username>
#
# The username referred to here is the same as in password_file. It is
# not the clientid.
#
#
# If is also possible to define ACLs based on pattern substitution within the
# topic. The patterns available for substition are:
#
# %c to match the client id of the client
# %u to match the username of the client
#
# The substitution pattern must be the only text for that level of hierarchy.
#
# The form is the same as for the topic keyword, but using pattern as the
# keyword.
# Pattern ACLs apply to all users even if the "user" keyword has previously
# been given.
#
# If using bridges with usernames and ACLs, connection messages can be allowed
# with the following pattern:
# pattern write $SYS/broker/connection/%c/state
#
# pattern [read|write|readwrite] <topic>
#
# Example:
#
# pattern write sensor/%u/data
#
# If an plugin is used as well as acl_file, the plugin check will be
# made first.
#acl_file /etc/mosquitto/aclfile
启用了日志记录,启用了不允许密码登录。
添加用户:
可以通过工具进行创建用户,并按提示输入密码
mosquitto_passwd -c /etc/mosquitto/pwfile user1 按提示输入密码 -c会覆盖文件
mosquitto_passwd /etc/mosquitto/pwfile user1 按提示输入密码 没有-c只会添加
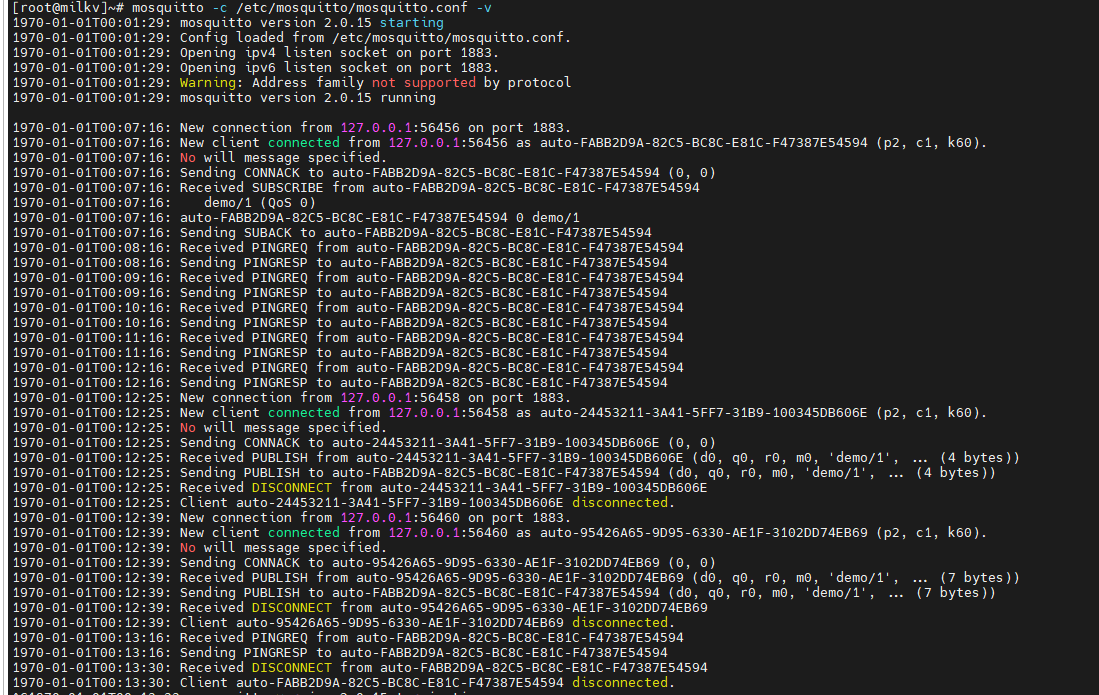
订阅主题:
mosquitto_sub -h localhost -t "test/#" -u user1 -P 123456 -i "client1" -d
发布消息:
mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t "test/abc" -u user2 -P 123456 -i "client2" -m "How are you?" -d
订阅系统状态
mosquitto_sub -h localhost -t '$SYS/broker/clients/active' -u user3 -P 123456 -i "client3" -d
订阅系统主题
MQTT客户端可以通过订阅位于$SYS层次下的主题来查看mosquitto服务器的状态信息。标记为Static的主题对于每一次订阅只发布一次。其它所有主题每隔sys_interval(在mosquitto.conf文件中配置)秒更新发布。如果sys_interval设置为0,系统就不发布更新。
$SYS中各主题说明如下:
$SYS/broker/bytes/received
自服务器启动以来共接收的字节数
$SYS/broker/bytes/sent
自服务器启动以来共发送的字节数
$SYS/broker/clients/connected,
$SYS/broker/clients/active (1.4版本已取消)
当前连接的客户端数量
$SYS/broker/clients/expired
超过有效期被断开连接的客户端数量,有效期通过persistent_client_expiration参数设置。
$SYS/broker/clients/disconnected,
$SYS/broker/clients/inactive (1.4版本已取消)
注册到服务器上的持久连接(clean seesion为假)但当前断开的客户端数量
$SYS/broker/clients/maximum
服务器同一时间连接的最大客户端数量
$SYS/broker/clients/total
有效和无效连接、注册到服务器上的总数。
$SYS/broker/connection/#
如果服务器设置了桥接,系统会提供一个主题来标识连接状态,默认使用$SYS/broker/connection/,如果主题值为1表示连接激活,如果为0表示连接没有激活。
$SYS/broker/heap/current size
Mosquitto正在使用的堆内存大小。注意这个主题是否可以使用取决于系统编译时的相关参数设置。
$SYS/broker/heap/maximum size
Mosquitto使用的最大堆内存。这个参数是否有效也取决于系统编译时的相关参数设置。
$SYS/broker/load/connections/+
不同时间段内服务器接收到的connections包的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。分别表示1分钟,5分钟,15分钟的平均数。
$SYS/broker/load/bytes/received/+
不同时间段内服务器接收数据的平均字节数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/bytes/sent/+
不同时间段内服务器发送数据的平均字节数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/messages/received/+
不同时间段内服务器接收到的所有类型消息的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/messages/sent/+
不同时间段内服务器发送的所有类型的消息的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/publish/dropped/+
不同时间段内服务器丢弃的消息的平均数,这表明了那些持久连接但与服务器断开的客户端失去消息的速率。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/publish/received/+
不同时间段内服务器接收的发布消息的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/publish/sent/+
不同时间段内服务器发送的发布消息的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/load/sockets/+
不同时间段内服务器打开的socket连接的平均数。最后的“+”可是1min,5min,15min。
$SYS/broker/messages/inflight
等待确认的Qos>0的消息的数量。
$SYS/broker/messages/received
自服务器启动以来接收的所有类型的消息总数。
$SYS/broker/messages/sent
自服务器启动以来发送的所有类型的消息总数。
$SYS/broker/messages/stored
服务器存储的消息的总数,包括保留消息和持久连接客户端的消息队列中的消息数。
$SYS/broker/publish/messages/dropped
由于inflight/queuing限制而直接丢弃的消息的总数,相关设置请查看mosquitto.conf中max_inflight_messages 和max_queued_messages参数。
$SYS/broker/publish/messages/received
自服务器启动以来接收的发布消息的总数。
$SYS/broker/publish/messages/sent
自服务器启动以来发送的发布消息的总数。
$SYS/broker/retained messages/count
服务器保留的消息总数。
$SYS/broker/subscriptions/count
服务器订阅主题总数。
$SYS/broker/timestamp
Mosquitto软件build的详细时间(Static)。
$SYS/broker/uptime
Mosquitto启动时长(单位:秒)。
$SYS/broker/version
Mosquitto软件版本号(Static)。
![]()
![]()